Hypertable
Hypertable is a high performance, open source, massively scalable database modeled after Bigtable, Google's proprietary, massively scalable database. Hypertable runs on top of a distributed file system such as the Apache HDFS, GlusterFS or the CloudStore Kosmos File System (KFS). It is written almost entirely in C++ as the developers believed it had significant performance advantages over Java.
History
Hypertable software was originally developed at the company Zvents before 2008. Doug Judd was a promoter of Hypertable. In January 2009, Baidu, the Chinese language search engine, became a project sponsor. A version 0.9.2.1 was described in a blog in February 2009. Development ended in March 2016.
- http://www.hypertable.com/blog/hypertable_inc._is_closing_its_doors
- https://www.networkworld.com/article/2283126/data-center/zvents-releases-open-source-cluster-database.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertable
- http://www.linux-mag.com/id/6645/
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120305120452/http://www.googlestack.com/50226711/taking_hypertable_0921_for_a_ride.php
Concurrency Control
Multi-version Concurrency Control (MVCC)
The system uses Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) and by default will auto-assign revision numbers using a timestamp.
Storage Architecture
Hypertable is capable of running on top of any filesystem. To achieve this, the system has abstracted the interface to the filesystem by sending all filesystem requests through a File System (FS) broker process. FS brokers have been developed for HDFS, MapR, Ceph, KFS, and local (for running on top of a local filesystem).
System Architecture
The diagram below provides a high-level overview of the Hypertable system followed by a brief description of each system component.
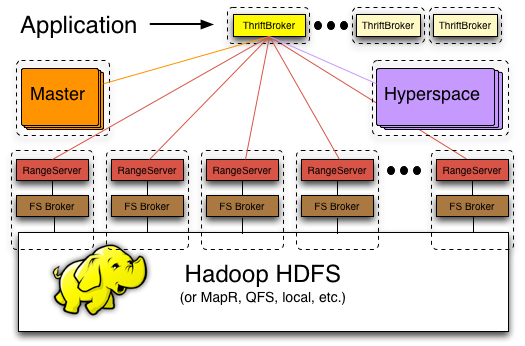
Hyperspace - This is Hypertable's equivalent to Google's Chubby service. Hyperspace is a lock manager and provides a filesystem for storing small amounts of metadata.
Master - The master handles all meta operations such as creating and deleting tables. The master is also responsible for detecting range server failures and re-assigning ranges if necessary.
Range Server - Range servers are responsible for managing ranges of table data, handling all reading and writing of data.
FS Broker - Hypertable is capable of running on top of any filesystem. To achieve this, the system has abstracted the interface to the filesystem by sending all filesystem requests through a File System (FS) broker process. The FS broker provides a normalized filesystem interface and translates normalized filesystem requests into native filesystem requests and vice-versa. FS brokers have been developed for HDFS, MapR, Ceph, KFS, and local (for running on top of a local filesystem).
ThriftBroker - Provides an interface for applications written in any high-level language to communicate with Hypertable. The ThriftBroker is implemented with Apache Thrift and provides bindings for applications written in Java, PHP, Ruby, Python, Perl, and C++.
Query Interface
Custom API Command-line / Shell
The Hypertable Query Language (HQL) allows you to create, modify, and query tables and invoke administrative commands. HQL is interpreted by the following interfaces: - The hypertable command line interface (ht shell), - The hql_exec and hql_query Thrift API methods, - The Hypertable::HqlInterpreter C++ class.
Website
Source Code
https://github.com/hypertable/hypertable
Tech Docs
http://www.hypertable.com/documentation/
Developer
Zvents
Country of Origin
Start Year
2008
End Year
2016
Acquired By
Baidu
Project Type
Written in
Supported languages
C++, Java, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby
