LedisDB
LedisDB is a NoSQL database written in Go. It is similar to Redis and uses redis protocol. It can be used as a replacement of Redis. However, it uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine. Therefore, unlike Redis, the storage is not limited by memory. The name LedisDB comes from Level-Redis-DB.
History
In 2014, Chinese programmer Siddon Tang noticed that as the number of users increases, the memory size is not enough for Redis. He found that SSDB could solve the problem. However, because of the three reasons below, he wanted to develop a database similar to SSDB using Go:
- Go development is quite rapid. Although the performance of Go is not as good as C++, it is great for rapid software development.
- He wanted to use LevelDB in his project and get some experience about LevelDB usage.
- He wanted to be more familiar with Redis.
Now, Siddon Tang is the Chief Engineer of PingCAP. He works on TiDB and TiKV. But LedisDB is still under his maintenance.
Compression
Dictionary Encoding Naïve (Page-Level)
LedisDB uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine. You can enable their compression feature via configuration. Data and index blocks are compressed individually. User can choose from a list of supported compression algorithms, like LZ4 and Snappy. User can choose to use Dictionary Compression, too. Data are decompressed when LedisDB retrieves them from the underlying storage engine.
Query Interface
Custom API HTTP / REST Command-line / Shell
LedisDB can be embedded in Go programs and programs can use its API to perform queries. LedisDB also provides a query interface in redis protocol called RESP(REdis Serialization Protocol), and can be queried via redis-cli. LedisDB has HTTP API support, too.
Concurrency Control
There is no concurrency control protocol in LedisDB because it does not support transactions. Like Redis, LedisDB processes requests as commands. Each command is treated as a single atomic operation. However, LedisDB does not provide any mechanism to combine commands into transactions.
Storage Architecture
Disk-oriented In-Memory Hybrid
LedisDB uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine and thus inherits their storage architecture. It also provides an option to use memory-backed storage (via goleveldb).
Checkpoints
Non-Blocking Consistent Blocking
LedisDB uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine and thus inherits their checkpoint mechanisms.
Storage Model
N-ary Storage Model (Row/Record)
LedisDB uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine and thus inherits their storage model. Data are stored in the form of ordered key-value pairs.
Indexes
Skip List Log-Structured Merge Tree
LedisDB uses RocksDB, LevelDB or goleveldb as storage engine and inherits their index data structure, which is the Log-Structured Merge Tree. They also use Skip List in the MemTable part.
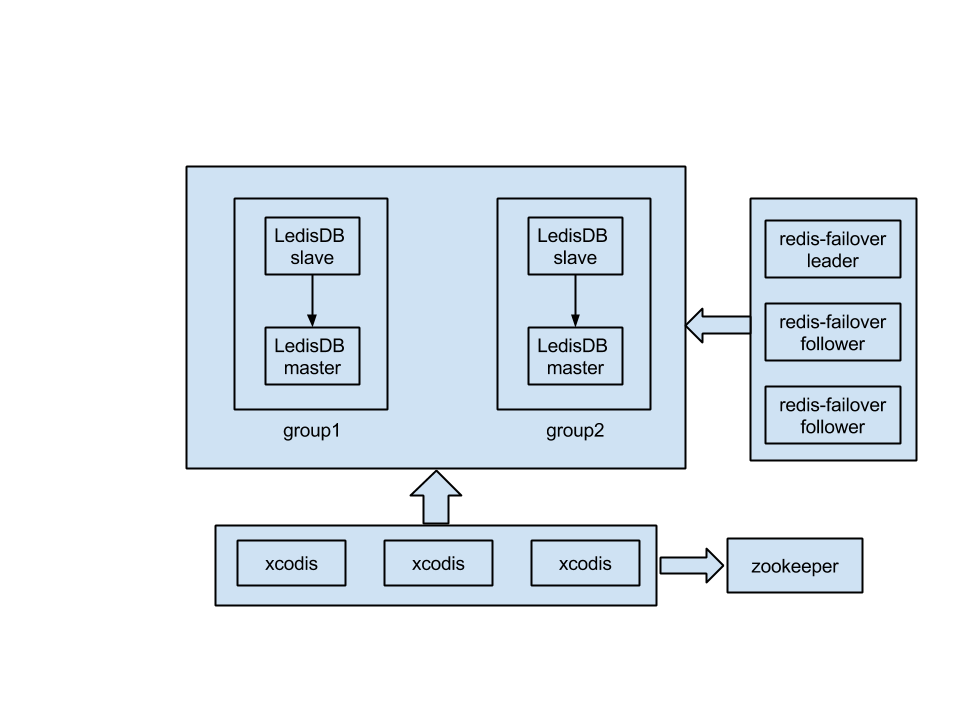
System Architecture
LedisDB can be embedded in Go programs. You can also run LedisDB as an independent server. Multiple LedisDB nodes and coordinator nodes can form a cluster with partition and Master-Replica replication. Each server does not share anything with others and only communicates with each other through network connection.
Website
Source Code
https://github.com/siddontang/ledisdb
Tech Docs
https://github.com/siddontang/ledisdb/wiki
Developer
Siddon Tang
Country of Origin
Start Year
2014
Project Type
Written in
Supported languages
C, Go, JavaScript, Lua, Python
